Hook: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "thumb|right|Hook operators in [[BQN]] A '''hook''' is an asymmetrical form of function composition that first applies one of the composed functions to one...") |
(Style changes to use APL instead of language-specific terminology) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Hooks.png|thumb|right|Hook operators in [[BQN]]]] | [[File:Hooks.png|thumb|right|Hook operators in [[BQN]]]] | ||
A '''hook''' is an asymmetrical form of function composition that first applies one of the composed functions to one argument, then applies the other function to one argument and the result. In [[J]], a 2-train is a hook, while [[I]] adds the mirror image to give two functions hook (<code>h</code>) and backhook (<code>H</code>). [[BQN]] uses two | A '''hook''' is an asymmetrical form of function composition that first applies one of the composed functions to one argument, then applies the other function to one argument and the result. In [[J]], a 2-[[train]] is a hook, while [[I]] adds the mirror image to give two functions (I has first-class functions but no operators) hook (<code>h</code>) and backhook (<code>H</code>). [[BQN]] uses two [[operator]]s Before (<code>⊸</code>) and After (<code>⟜</code>), which also serve the purpose of the [[Bind]] operator. | ||
The meaning of 2-train as hook was first proposed in [[Ken Iverson|Iverson]] and [[Eugene McDonnell|McDonnell]]'s paper ''Phrasal Forms'' introducing [[train]]s<ref>[[Ken Iverson]] and [[Eugene McDonnell]]. [http://www.jsoftware.com/papers/fork.htm Phrasal forms] at [[APL89]].</ref>, and soon included in [[J]]. This definition specifies that <source lang=j inline>(F G) y</source> is <source lang=j inline>y F G y</source> and <source lang=j inline>x (F G) y</source> is <source lang=j inline>x F G y</source>. However, [[Roger Hui]] later opined that this definition was better suited to a | The meaning of 2-train as hook was first proposed in [[Ken Iverson|Iverson]] and [[Eugene McDonnell|McDonnell]]'s paper ''Phrasal Forms'' introducing [[train]]s<ref>[[Ken Iverson]] and [[Eugene McDonnell]]. [http://www.jsoftware.com/papers/fork.htm Phrasal forms] at [[APL89]].</ref>, and soon included in [[J]]. This definition specifies that <source lang=j inline>(F G) y</source> is <source lang=j inline>y F G y</source> and <source lang=j inline>x (F G) y</source> is <source lang=j inline>x F G y</source>. However, [[Roger Hui]] later opined that this definition was better suited to a dyadic operator than an element of syntax,<ref>[[Roger Hui]]. [https://code.jsoftware.com/wiki/Essays/Hook_Conjunction%3F Hook Conjunction?]. J Wiki essays. 2006. Accessed 2021-02-08.</ref> and defined to 2-train to represent [[Atop]] instead when he led the introduction of trains to [[Dyalog APL]]. | ||
In [[I]] and [[BQN]], there are two hooks in order to maintain symmetry: for example, BQN defines Before (<code>⊸</code>) to be the | In [[I]] and [[BQN]], there are two hooks in order to maintain symmetry: for example, BQN defines Before (<code>⊸</code>) to be the dyadic operator <code>{(𝔽𝕨⊣𝕩)𝔾𝕩}</code> ("<code>𝔾</code>'s left argument comes from <code>𝔽</code>") and After (<code>⟜</code>) to be <code>{(𝕨⊣𝕩)𝔽𝔾𝕩}</code> ("<code>𝔽</code>'s right argument comes from <code>𝔾</code>"). In the dyadic case these functions are identical to [[Reverse Compose]] and [[Beside]] respectively, but in the monadic case they differ because the argument is used twice: the second function application takes it as an argument directly in addition to the result of the first function application. | ||
Like [[Reverse Compose]], the two hooks can be used together to form a [[split-compose]] construct. | Like [[Reverse Compose]], the two hooks can be used together to form a [[split-compose]] construct. | ||
Revision as of 20:17, 8 February 2021
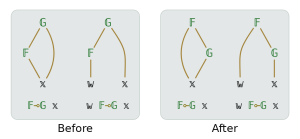
A hook is an asymmetrical form of function composition that first applies one of the composed functions to one argument, then applies the other function to one argument and the result. In J, a 2-train is a hook, while I adds the mirror image to give two functions (I has first-class functions but no operators) hook (h) and backhook (H). BQN uses two operators Before (⊸) and After (⟜), which also serve the purpose of the Bind operator.
The meaning of 2-train as hook was first proposed in Iverson and McDonnell's paper Phrasal Forms introducing trains[1], and soon included in J. This definition specifies that (F G) y is y F G y and x (F G) y is x F G y. However, Roger Hui later opined that this definition was better suited to a dyadic operator than an element of syntax,[2] and defined to 2-train to represent Atop instead when he led the introduction of trains to Dyalog APL.
In I and BQN, there are two hooks in order to maintain symmetry: for example, BQN defines Before (⊸) to be the dyadic operator {(𝔽𝕨⊣𝕩)𝔾𝕩} ("𝔾's left argument comes from 𝔽") and After (⟜) to be {(𝕨⊣𝕩)𝔽𝔾𝕩} ("𝔽's right argument comes from 𝔾"). In the dyadic case these functions are identical to Reverse Compose and Beside respectively, but in the monadic case they differ because the argument is used twice: the second function application takes it as an argument directly in addition to the result of the first function application.
Like Reverse Compose, the two hooks can be used together to form a split-compose construct.
3‿¯1‿4 ×⊸×⟜| ¯2‿¯7‿1 ⟨ 2 ¯7 1 ⟩
This definition behaves differently that the Compose-based one when only one argument is given: in that case, it becomes a monadic 3-train.
The name "hook" was chosen based on the hook shape of a function call diagram such as the one below, taken from Phrasal Forms.
⍺(fg)⍵ ←→ ⍺fg⍵
f
/ \
⍺ g
\
⍵
See also
External links
References
- ↑ Ken Iverson and Eugene McDonnell. Phrasal forms at APL89.
- ↑ Roger Hui. Hook Conjunction?. J Wiki essays. 2006. Accessed 2021-02-08.