Simple examples: Difference between revisions
(The specific dialects are not important here, and the "try it" link doesn't actually try it.) |
m (Text replacement - "<source" to "<syntaxhighlight") |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Here is an APL program to calculate the average (arithmetic mean) of a list of numbers, written as a [[dfn]]: | Here is an APL program to calculate the average (arithmetic mean) of a list of numbers, written as a [[dfn]]: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
{(+⌿⍵)÷≢⍵} | {(+⌿⍵)÷≢⍵} | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
It is unnamed: the enclosing braces mark it as a function definition. It can be assigned a name for use later, or used anonymously in a more complex expression. | It is unnamed: the enclosing braces mark it as a function definition. It can be assigned a name for use later, or used anonymously in a more complex expression. | ||
The < | The <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source> refers to the argument of the function, a list (or 1-dimensional array) of numbers. The <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≢</source> denotes the [[tally]] function, which returns here the length of (number of elements in) the argument <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source>. The divide symbol <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>÷</source> has its usual meaning. | ||
The parenthesised < | The parenthesised <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+⌿⍵</source> denotes the sum of all the elements of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source>. The <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⌿</source> operator combines with the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+</source> function: the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⌿</source> fixes the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+</source> function between each element of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source>, so that | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
+⌿ 1 2 3 4 5 6 | +⌿ 1 2 3 4 5 6 | ||
21 | 21 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
is the same as | is the same as | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
1+2+3+4+5+6 | 1+2+3+4+5+6 | ||
21 | 21 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Operators === | === Operators === | ||
[[Operator]]s like < | [[Operator]]s like <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⌿</source> can be used to derive new functions not only from [[primitive function]]s like <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+</source>, but also from defined functions. For example | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
{⍺,', ',⍵}⌿ | {⍺,', ',⍵}⌿ | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
will transform a list of strings representing words into a comma-separated list: | will transform a list of strings representing words into a comma-separated list: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
{⍺,', ',⍵}⌿'cow' 'sheep' 'cat' 'dog' | {⍺,', ',⍵}⌿'cow' 'sheep' 'cat' 'dog' | ||
┌────────────────────┐ | ┌────────────────────┐ | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
└────────────────────┘ | └────────────────────┘ | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
So back to our mean example. < | So back to our mean example. <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>(+⌿⍵)</source> gives the sum of the list, which is then divided by <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≢⍵</source>, the number elements in it. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
{(+⌿⍵)÷≢⍵} 3 4.5 7 21 | {(+⌿⍵)÷≢⍵} 3 4.5 7 21 | ||
8.875 | 8.875 | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
In APL’s tacit definition, no braces are needed to mark the definition of a function: primitive functions just combine in a way that enables us to omit any reference to the function arguments — hence ''tacit''. Here is the same calculation written tacitly: | In APL’s tacit definition, no braces are needed to mark the definition of a function: primitive functions just combine in a way that enables us to omit any reference to the function arguments — hence ''tacit''. Here is the same calculation written tacitly: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
(+⌿÷≢) 3 4.5 7 21 | (+⌿÷≢) 3 4.5 7 21 | ||
8.875 | 8.875 | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
This is a so called 3-train, also known as a ''fork''. It is evaluated like this: | This is a so called 3-train, also known as a ''fork''. It is evaluated like this: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|< | |<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(+⌿ ÷ ≢) 3 4.5 7 21</source>|| {{←→}} ||<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(+⌿ 3 4.5 7 21) ÷ (≢ 3 4.5 7 21)</source> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Note that < | Note that <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+⌿</source> is evaluated as a single derived function. | ||
The general scheme for monadic 3-trains is the following: | The general scheme for monadic 3-trains is the following: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|< | |<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(f g h) ⍵</source>|| {{←→}} ||<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(f ⍵) g (h ⍵)</source> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
APL represents text as character lists (vectors), making many text operations trivial. | APL represents text as character lists (vectors), making many text operations trivial. | ||
=== Split text by delimiter === | === Split text by delimiter === | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≠</source> gives 1 for true and 0 for false. It [[scalar function|pairs up]] a single element argument with all the elements of the other arguments: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
','≠'comma,delimited,text' | ','≠'comma,delimited,text' | ||
1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⊢</source> returns its right argument: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
','⊢'comma,delimited,text' | ','⊢'comma,delimited,text' | ||
comma,delimited,text | comma,delimited,text | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⊆</source> returns a list of runs as indicated by runs of 1s, leaving out elements indicated by 0s: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
1 1 0 1 1 1⊆'Hello!' | 1 1 0 1 1 1⊆'Hello!' | ||
┌──┬───┐ | ┌──┬───┐ | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
[https://tryapl.org/?a=%27%2C%27%28%u2260%u2286%u22A2%29%27comma%2Cdelimited%2Ctext%27&run Try it now!] | [https://tryapl.org/?a=%27%2C%27%28%u2260%u2286%u22A2%29%27comma%2Cdelimited%2Ctext%27&run Try it now!] | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
','(≠⊆⊢)'comma,delimited,text' | ','(≠⊆⊢)'comma,delimited,text' | ||
┌─────┬─────────┬────┐ | ┌─────┬─────────┬────┐ | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
{{Works in|[[Dyalog APL]]}} | {{Works in|[[Dyalog APL]]}} | ||
Notice that you can read the [[tacit]] function < | Notice that you can read the [[tacit]] function <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≠⊆⊢</source> like an English sentence: ''The inequality partitions the right argument''. | ||
Many dialects do not support the above [[tacit]] syntax, and use the [[glyph]] < | Many dialects do not support the above [[tacit]] syntax, and use the [[glyph]] <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⊂</source> for partition [[primitive function]]. In such dialects, the following formulation can be used: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
(','≠s)⊂s←'comma,delimited,text' | (','≠s)⊂s←'comma,delimited,text' | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
{{Works in|[[APL2]], [[APLX]], [[GNU APL]]}} | {{Works in|[[APL2]], [[APLX]], [[GNU APL]]}} | ||
This assigns the text to the variable < | This assigns the text to the variable <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>s</source>, then separately computes the partitioning vector and applies it. | ||
=== Indices of multiple elements === | === Indices of multiple elements === | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>∊</source> gives us a mask for elements (characters) in the left argument that are members of the right argument: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
'mississippi'∊'sp' | 'mississippi'∊'sp' | ||
0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 | 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍸</source> gives us the indices where true (1): | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
⍸'mississippi'∊'sp' | ⍸'mississippi'∊'sp' | ||
3 4 6 7 9 10 | 3 4 6 7 9 10 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
We can combine this into an anonymous infix (dyadic) function: | We can combine this into an anonymous infix (dyadic) function: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
'mississippi' (⍸∊) 'sp' | 'mississippi' (⍸∊) 'sp' | ||
3 4 6 7 9 10 | 3 4 6 7 9 10 | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
=== Frequency of characters in a string === | === Frequency of characters in a string === | ||
The [[Outer Product]] allows for an intuitive way to compute the occurrence of characters at a given location in a string: | The [[Outer Product]] allows for an intuitive way to compute the occurrence of characters at a given location in a string: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
'abcd' ∘.= 'cabbage' | 'abcd' ∘.= 'cabbage' | ||
0 1 0 0 1 0 0 | 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 | ||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Then it is simply a matter of performing a sum-reduce < | Then it is simply a matter of performing a sum-reduce <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+/</source> to calculate the total frequency of each character:<ref name="Marshall LambaConf 2019">[[Marshall Lochbaum]] used this example as part of his talk on [[Outer Product]] at LambdaConf 2019.</ref> | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
+/ 'abcd' ∘.= 'cabbage' | +/ 'abcd' ∘.= 'cabbage' | ||
2 2 1 0 | 2 2 1 0 | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
What was the one-liner for the nesting level of parentheses? It would take a bit of work to figure out, because at the time of the meeting Perlis described, no APL implementation existed. Two possibilities are explained here. | What was the one-liner for the nesting level of parentheses? It would take a bit of work to figure out, because at the time of the meeting Perlis described, no APL implementation existed. Two possibilities are explained here. | ||
==== Method A ==== | ==== Method A ==== | ||
For this more complex computation, we can expand on the previous example's use of < | For this more complex computation, we can expand on the previous example's use of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>∘.=</source>. First we compare all characters to the opening and closing characters; | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))' | '()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))' | ||
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
An opening increases the current level, while a closing decreases, so we convert this to ''changes'' (or ''deltas'') by subtracting the bottom row from the top row: | An opening increases the current level, while a closing decreases, so we convert this to ''changes'' (or ''deltas'') by subtracting the bottom row from the top row: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
-⌿'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))' | -⌿'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))' | ||
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ¯1 ¯1 ¯1 | 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ¯1 ¯1 ¯1 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
The running sum is what we're looking for: | The running sum is what we're looking for: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
+\-⌿'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))' | +\-⌿'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))' | ||
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 2 1 | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 2 1 | ||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
{{Works in|all APLs}} | {{Works in|all APLs}} | ||
==== Method B ==== | ==== Method B ==== | ||
Alternatively, we can utilise that if the [[Index Of]] function < | Alternatively, we can utilise that if the [[Index Of]] function <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍳</source> doesn't find what it is looking for, it returns the next index after the last element in the the lookup array: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
'ABBA'⍳'ABC' | 'ABBA'⍳'ABC' | ||
1 2 5 | 1 2 5 | ||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Whenever we have a 1 the parenthesis level increases, and when we have a 2 it decreases. If we have a 3, it remains as-is. We can do this mapping by indexing into these values: | Whenever we have a 1 the parenthesis level increases, and when we have a 2 it decreases. If we have a 3, it remains as-is. We can do this mapping by indexing into these values: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
1 ¯1 0['()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'] | 1 ¯1 0['()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'] | ||
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ¯1 ¯1 ¯1 | 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ¯1 ¯1 ¯1 | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
The running sum is what we're looking for: | The running sum is what we're looking for: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
+\1 ¯1 0['()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'] | +\1 ¯1 0['()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'] | ||
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 2 1 | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 2 1 | ||
| Line 180: | Line 180: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
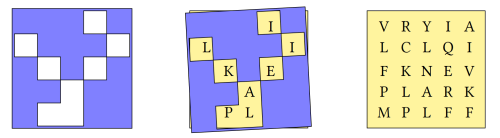
Represent both the grid of letters and the grille as character matrices. | Represent both the grid of letters and the grille as character matrices. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
⎕←(grid grille)←5 5∘⍴¨'VRYIALCLQIFKNEVPLARKMPLFF' '⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺' | ⎕←(grid grille)←5 5∘⍴¨'VRYIALCLQIFKNEVPLARKMPLFF' '⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺' | ||
┌─────┬─────┐ | ┌─────┬─────┐ | ||
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
Retrieve elements of the grid where there are spaces in the grille. | Retrieve elements of the grid where there are spaces in the grille. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
grid[⍸grille=' '] | grid[⍸grille=' '] | ||
ILIKEAPL | ILIKEAPL | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
An alternative method using [[ravel]]. | An alternative method using [[ravel]]. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | ||
(' '=,grille)/,grid | (' '=,grille)/,grid | ||
ILIKEAPL | ILIKEAPL | ||
Revision as of 22:08, 10 September 2022
This page contains examples that show APL's strengths. The examples require minimal background and have no special dependencies. If these examples are too simple for you, have a look at our advanced examples.
Arithmetic mean
Here is an APL program to calculate the average (arithmetic mean) of a list of numbers, written as a dfn: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
{(+⌿⍵)÷≢⍵}
</source> It is unnamed: the enclosing braces mark it as a function definition. It can be assigned a name for use later, or used anonymously in a more complex expression.
The <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source> refers to the argument of the function, a list (or 1-dimensional array) of numbers. The <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≢</source> denotes the tally function, which returns here the length of (number of elements in) the argument <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source>. The divide symbol <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>÷</source> has its usual meaning.
The parenthesised <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+⌿⍵</source> denotes the sum of all the elements of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source>. The <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⌿</source> operator combines with the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+</source> function: the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⌿</source> fixes the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+</source> function between each element of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍵</source>, so that <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
+⌿ 1 2 3 4 5 6
21 </source> is the same as <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
1+2+3+4+5+6
21 </source>
Operators
Operators like <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⌿</source> can be used to derive new functions not only from primitive functions like <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+</source>, but also from defined functions. For example <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
{⍺,', ',⍵}⌿
</source> will transform a list of strings representing words into a comma-separated list: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
{⍺,', ',⍵}⌿'cow' 'sheep' 'cat' 'dog'
┌────────────────────┐ │cow, sheep, cat, dog│ └────────────────────┘ </source> So back to our mean example. <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>(+⌿⍵)</source> gives the sum of the list, which is then divided by <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≢⍵</source>, the number elements in it. <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
{(+⌿⍵)÷≢⍵} 3 4.5 7 21
8.875 </source>
Tacit programming
- Main article: Tacit programming
In APL’s tacit definition, no braces are needed to mark the definition of a function: primitive functions just combine in a way that enables us to omit any reference to the function arguments — hence tacit. Here is the same calculation written tacitly: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
(+⌿÷≢) 3 4.5 7 21
8.875 </source>
This is a so called 3-train, also known as a fork. It is evaluated like this:
| <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(+⌿ ÷ ≢) 3 4.5 7 21</source> | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(+⌿ 3 4.5 7 21) ÷ (≢ 3 4.5 7 21)</source> |
Note that <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+⌿</source> is evaluated as a single derived function. The general scheme for monadic 3-trains is the following:
| <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(f g h) ⍵</source> | <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(f ⍵) g (h ⍵)</source> |
But other types of trains are also possible.
Text processing
APL represents text as character lists (vectors), making many text operations trivial.
Split text by delimiter
<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≠</source> gives 1 for true and 0 for false. It pairs up a single element argument with all the elements of the other arguments: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
','≠'comma,delimited,text'
1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 </source> <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⊢</source> returns its right argument: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
','⊢'comma,delimited,text'
comma,delimited,text </source> <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⊆</source> returns a list of runs as indicated by runs of 1s, leaving out elements indicated by 0s: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
1 1 0 1 1 1⊆'Hello!'
┌──┬───┐ │He│lo!│ └──┴───┘ </source> We use the comparison vector to partition the right argument:
Try it now! <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
','(≠⊆⊢)'comma,delimited,text'
┌─────┬─────────┬────┐ │comma│delimited│text│ └─────┴─────────┴────┘ </source>
Notice that you can read the tacit function <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≠⊆⊢</source> like an English sentence: The inequality partitions the right argument.
Many dialects do not support the above tacit syntax, and use the glyph <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⊂</source> for partition primitive function. In such dialects, the following formulation can be used: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
(','≠s)⊂s←'comma,delimited,text'
</source>
This assigns the text to the variable <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>s</source>, then separately computes the partitioning vector and applies it.
Indices of multiple elements
<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>∊</source> gives us a mask for elements (characters) in the left argument that are members of the right argument: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
'mississippi'∊'sp'
0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 </source> <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍸</source> gives us the indices where true (1): <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
⍸'mississippi'∊'sp'
3 4 6 7 9 10 </source> We can combine this into an anonymous infix (dyadic) function: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
'mississippi' (⍸∊) 'sp'
3 4 6 7 9 10 </source>
Frequency of characters in a string
The Outer Product allows for an intuitive way to compute the occurrence of characters at a given location in a string: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
'abcd' ∘.= 'cabbage' 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
</source> Then it is simply a matter of performing a sum-reduce <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>+/</source> to calculate the total frequency of each character:[1] <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
+/ 'abcd' ∘.= 'cabbage' 2 2 1 0
</source>
Parenthesis nesting level
"Ken was showing some slides — and one of his slides had something on it that I was later to learn was an APL one-liner. And he tossed this off as an example of the expressiveness of the APL notation. I believe the one-liner was one of the standard ones for indicating the nesting level of the parentheses in an algebraic expression. But the one-liner was very short — ten characters, something like that — and having been involved with programming things like that for a long time and realizing that it took a reasonable amount of code to do, I looked at it and said, “My God, there must be something in this language.”"
Alan Perlis. Almost Perfect Artifacts Improve only in Small Ways: APL is more French than English at APL78.
What was the one-liner for the nesting level of parentheses? It would take a bit of work to figure out, because at the time of the meeting Perlis described, no APL implementation existed. Two possibilities are explained here.
Method A
For this more complex computation, we can expand on the previous example's use of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>∘.=</source>. First we compare all characters to the opening and closing characters; <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 </source> An opening increases the current level, while a closing decreases, so we convert this to changes (or deltas) by subtracting the bottom row from the top row: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
-⌿'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ¯1 ¯1 ¯1 </source> The running sum is what we're looking for: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
+\-⌿'()'∘.='plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 2 1 </source>
Method B
Alternatively, we can utilise that if the Index Of function <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍳</source> doesn't find what it is looking for, it returns the next index after the last element in the the lookup array: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
'ABBA'⍳'ABC'
1 2 5
'()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))'
3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 2 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 2 2 2 </source> Whenever we have a 1 the parenthesis level increases, and when we have a 2 it decreases. If we have a 3, it remains as-is. We can do this mapping by indexing into these values: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
1 ¯1 0['()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))']
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ¯1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ¯1 ¯1 ¯1 </source> The running sum is what we're looking for: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
+\1 ¯1 0['()'⍳'plus(square(a),plus(square(b),times(2,plus(a,b)))']
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 2 1 </source>
Grille cypher
A grille is a 500 year old method for encrypting messages.
Represent both the grid of letters and the grille as character matrices. <syntaxhighlight lang=apl> ⎕←(grid grille)←5 5∘⍴¨'VRYIALCLQIFKNEVPLARKMPLFF' '⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺' ┌─────┬─────┐ │VRYIA│⌺⌺⌺ ⌺│ │LCLQI│ ⌺⌺⌺ │ │FKNEV│⌺ ⌺ ⌺│ │PLARK│⌺⌺ ⌺⌺│ │MPLFF│⌺ ⌺⌺│ └─────┴─────┘ </source>
Retrieve elements of the grid where there are spaces in the grille. <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
grid[⍸grille=' ']
ILIKEAPL </source> An alternative method using ravel. <syntaxhighlight lang=apl>
(' '=,grille)/,grid
ILIKEAPL </source>
References
- ↑ Marshall Lochbaum used this example as part of his talk on Outer Product at LambdaConf 2019.
| APL development [edit] | |
|---|---|
| Interface | Session ∙ Typing glyphs (on Linux) ∙ Fonts ∙ Text editors |
| Publications | Introductions ∙ Learning resources ∙ Simple examples ∙ Advanced examples ∙ Mnemonics ∙ ISO 8485:1989 ∙ ISO/IEC 13751:2001 ∙ A Dictionary of APL ∙ Case studies ∙ Documentation suites ∙ Books ∙ Papers ∙ Videos ∙ APL Quote Quad ∙ Vector journal ∙ Terminology (Chinese, German) ∙ Neural networks ∙ Error trapping with Dyalog APL (in forms) |
| Sharing code | Backwards compatibility ∙ APLcart ∙ APLTree ∙ APL-Cation ∙ Dfns workspace ∙ Tatin ∙ Cider |
| Implementation | Resources ∙ Open-source ∙ Magic function ∙ Performance ∙ APL hardware |
| Developers | Timeline of corporations ∙ APL2000 ∙ Dyalog ∙ IBM ∙ IPSA ∙ STSC |