Typing glyphs: Difference between revisions
(android) |
(Reorganize page content to prioritize instructing readers on how to set up an APL keyboard. It is very much a WIP (would like to add instructions for more desktop environments, for example)) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
APL uses a large range of [[glyphs|special graphic symbols]] to represent most functions and operators. While keyboard mappings become memorized over time, entering APL characters can frustrate the beginner. However, a study involving high school students found that typing and using APL characters did not hinder the students in any measurable way. There are several convenient ways to enter the glyphs. | APL uses a large range of [[glyphs|special graphic symbols]] to represent most functions and operators. While keyboard mappings become memorized over time, entering APL characters can frustrate the beginner. However, a study involving high school students found that typing and using APL characters did not hinder the students in any measurable way. There are several convenient ways to enter the glyphs. | ||
== Keyboard | == How to Set up an APL Keyboard == | ||
Most of today's APLs use a mapping which derives from the original [[APL\360]] terminals' keyboard layout. For example, | === Linux === | ||
[[Geoff Streeter]] authored a paper, [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/conference/dyalog10/presentations/P19_Streeter_Keyboards.pdf Supporting APL keyboards on Linux], which was presented at the [https://aplwiki.com/wiki/Dyalog_user_meeting#Dyalog_.2710 Dyalog '10] user meeting. In this paper, Geoff details how APL keyboards can be supported in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X_Window_System X11] using <code>xkb</code>, the [https://www.x.org/wiki/XKB/ X Keyboard Extension]. | |||
Most Linux distributions released after mid-2012 have [https://forums.dyalog.com/viewtopic.php?f=20&t=210 Dyalog keyboard support] included with the distribution. | |||
==== setxkbmap ==== | |||
The simplest way to set up an APL keyboard on Linux is with the following <code>setxkbmap</code> command. Enter the following in your terminal emulator of choice: | |||
<pre> | |||
setxkbmap -layout us,apl -variant ,dyalog -option grp:switch | |||
</pre> | |||
An explanation: | |||
* <code>-layout us,apl</code> assigns <code>us</code> ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_English U.S. English]) to be the primary layout, whereas <code>apl</code> is secondary | |||
* <code>-option grp:switch</code> assigns <kbd>Right Alt</kbd> to switch to the secondary <code>apl</code> layout when it is pressed, otherwise <code>us</code> is used | |||
* <code>-variant ,dyalog</code> assigns the [[Dyalog APL]] variant to the <code>apl</code> layout which contains modifiations unique to the Dyalog language ('''Note the preceding comma''') | |||
A full list of keys that can be used to switch layouts is included in <code>/usr/share/X11/xkb/rules/evdev.lst</code> under the <code>option</code> category. | |||
'''Note:''' these changes are not permanent; the user will have to select one of a myriad of methods to run the command on startup. Alternatively, if they use one of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Desktop_environment desktop environments] listed below, they can follow those instructions. | |||
==== Xfce ==== | |||
A tutorial specific to Xfce's config files can be found [https://github.com/hashslingrz/apl-keyboard-xfce at this GitHub repository]. | |||
=== Windows === | |||
* [[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://github.com/abrudz/Kbd keyboard layouts for Windows], which uses <kbd>AltGr</kbd>. | |||
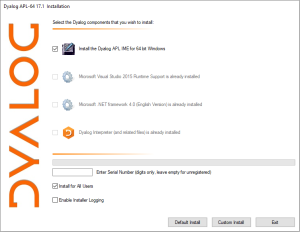
* The [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#tab-1 Dyalog Unicode IME] uses <kbd>Ctrl</kbd>. It is also possible to install the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Input_method IME] alongside a regular [[Dyalog APL]] installation: | |||
[[File:Dyalog_APL_Installer.png|frameless|Dyalog APL IME selected in installer]] | |||
== Approaches to Layout and Input == | |||
Most of today's APLs use a mapping which derives from the original [[APL\360]] terminals' keyboard layout. For example, Dyalog APL's standard US English layout for is as follows: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬─────────┐ | ┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬─────────┐ | ||
| Line 21: | Line 55: | ||
Additional charts for other layouts are [https://dfns.dyalog.com/n_keyboards.htm available]. | Additional charts for other layouts are [https://dfns.dyalog.com/n_keyboards.htm available]. | ||
There are multiple | There are multiple ways to access the glyphs associated with a particular key. | ||
=== Text editors === | === Text editors === | ||
| Line 37: | Line 71: | ||
* [[APLX]] uses <kbd>AltGr</kbd> with an option to also use <kbd>Alt</kbd> | * [[APLX]] uses <kbd>AltGr</kbd> with an option to also use <kbd>Alt</kbd> | ||
for example, openSUSE 12.2, Ubuntu 12.10 and Fedora 17. | |||
=== Prefix key === | === Prefix key === | ||
| Line 56: | Line 88: | ||
* dzaima's [https://github.com/dzaima/hackerskeyboard Hacker's Keyboard + APL language] using long-press to access APL glyphs. | * dzaima's [https://github.com/dzaima/hackerskeyboard Hacker's Keyboard + APL language] using long-press to access APL glyphs. | ||
= | === Keyword look-up === | ||
== Keyword look-up == | |||
* The [https://github.com/Dyalog/ride/releases/latest Dyalog RIDE] (Remote Integrated Development Environment) allows hitting the prefix key (<kbd>`</kbd> by default, but configurable) twice, followed by the (beginning of the) name of a symbol or a functionality. It then displays a drop-down of choices with arrow keys to indicate choice and the Tab key to insert the symbol. E.g. <kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>d</kbd>,<kbd>i</kbd>,<kbd>v</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> inserts <source lang=apl inline>÷</source>. | * The [https://github.com/Dyalog/ride/releases/latest Dyalog RIDE] (Remote Integrated Development Environment) allows hitting the prefix key (<kbd>`</kbd> by default, but configurable) twice, followed by the (beginning of the) name of a symbol or a functionality. It then displays a drop-down of choices with arrow keys to indicate choice and the Tab key to insert the symbol. E.g. <kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>d</kbd>,<kbd>i</kbd>,<kbd>v</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> inserts <source lang=apl inline>÷</source>. | ||
== ASCII symbol combination == | === ASCII symbol combination === | ||
* Many APL glyphs can be approximated by overlaying or juxtaposing two ASCII characters. [[ngn/apl]]'s scripted demo interface and [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar] allow such a pair of characters and hitting the Tab key to replace them with the corresponding APL character. For example, <kbd><</kbd>,<kbd>-</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> will insert <source lang=apl inline>←</source> and <kbd>T</kbd>,<kbd>o</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> will insert <source lang=apl inline>⍕</source>. | * Many APL glyphs can be approximated by overlaying or juxtaposing two ASCII characters. [[ngn/apl]]'s scripted demo interface and [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar] allow such a pair of characters and hitting the Tab key to replace them with the corresponding APL character. For example, <kbd><</kbd>,<kbd>-</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> will insert <source lang=apl inline>←</source> and <kbd>T</kbd>,<kbd>o</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> will insert <source lang=apl inline>⍕</source>. | ||
== On-screen language bar == | === On-screen language bar === | ||
Several APL IDEs allow the display of a toolbar with a button for each APL glyph: | Several APL IDEs allow the display of a toolbar with a button for each APL glyph: | ||
| Line 78: | Line 102: | ||
* [[Dyalog APL]], [[NARS2000]], [[APL2]] and [[ngn/apl]]'s scripted demo interface all have this feature. | * [[Dyalog APL]], [[NARS2000]], [[APL2]] and [[ngn/apl]]'s scripted demo interface all have this feature. | ||
=== Web browsers === | ==== Web browsers ==== | ||
* [[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl in-browser language bar] adds this to most web pages on demand. | * [[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl in-browser language bar] adds this to most web pages on demand. | ||
| Line 85: | Line 109: | ||
{{APL glyphs}} | {{APL glyphs}} | ||
[[Category:APL character set]] | [[Category:APL character set]] | ||
== Hardware APL keyboard == | |||
A couple of hardware keyboards are being sold with APL symbols pre-printed onto the key caps: | |||
* Dyalog sells [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#mainContent US English, UK English, and Danish keyboards]. | |||
* Unicomp sells both [https://www.amazon.com/Unicomp-Classic-Buckling-Spring-Keyboard/dp/B01M7V3M61/ref=sr_1_8 entire keyboards] and [https://www.pckeyboard.com/page/product/USAPLSET separate key caps] for their keyboard range. | |||
Revision as of 10:55, 13 May 2020
APL uses a large range of special graphic symbols to represent most functions and operators. While keyboard mappings become memorized over time, entering APL characters can frustrate the beginner. However, a study involving high school students found that typing and using APL characters did not hinder the students in any measurable way. There are several convenient ways to enter the glyphs.
How to Set up an APL Keyboard
Linux
Geoff Streeter authored a paper, Supporting APL keyboards on Linux, which was presented at the Dyalog '10 user meeting. In this paper, Geoff details how APL keyboards can be supported in X11 using xkb, the X Keyboard Extension.
Most Linux distributions released after mid-2012 have Dyalog keyboard support included with the distribution.
setxkbmap
The simplest way to set up an APL keyboard on Linux is with the following setxkbmap command. Enter the following in your terminal emulator of choice:
setxkbmap -layout us,apl -variant ,dyalog -option grp:switch
An explanation:
-layout us,aplassignsus(U.S. English) to be the primary layout, whereasaplis secondary-option grp:switchassigns Right Alt to switch to the secondaryapllayout when it is pressed, otherwiseusis used-variant ,dyalogassigns the Dyalog APL variant to theapllayout which contains modifiations unique to the Dyalog language (Note the preceding comma)
A full list of keys that can be used to switch layouts is included in /usr/share/X11/xkb/rules/evdev.lst under the option category.
Note: these changes are not permanent; the user will have to select one of a myriad of methods to run the command on startup. Alternatively, if they use one of the desktop environments listed below, they can follow those instructions.
Xfce
A tutorial specific to Xfce's config files can be found at this GitHub repository.
Windows
- Adám Brudzewsky's keyboard layouts for Windows, which uses AltGr.
- The Dyalog Unicode IME uses Ctrl. It is also possible to install the IME alongside a regular Dyalog APL installation:
Approaches to Layout and Input
Most of today's APLs use a mapping which derives from the original APL\360 terminals' keyboard layout. For example, Dyalog APL's standard US English layout for is as follows:
┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬─────────┐
│~ ⌺ │! ⌶ │@ ⍫ │# ⍒ │$ ⍋ │% ⌽ │^ ⍉ │& ⊖ │* ⍟ │( ⍱ │) ⍲ │_ ! │+ ⌹ │Backspace│
│` ⋄ │1 ¨ │2 ¯ │3 < │4 ≤ │5 = │6 ≥ │7 > │8 ≠ │9 ∨ │0 ∧ │- × │= ÷ │ │
├────┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬──────┤
│Tab │Q │W │E ⍷ │R │T ⍨ │Y │U │I ⍸ │O ⍥ │P ⍣ │{ ⍞ │} ⍬ │| ⊣ │
│ │q ? │w ⍵ │e ∊ │r ⍴ │t ~ │y ↑ │u ↓ │i ⍳ │o ○ │p * │[ ← │] → │\ ⊢ │
├───────┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴──────┤
│Caps │A │S │D │F │G │H │J ⍤ │K ⌸ │L ⌷ │: ≡ │" ≢ │Enter │
│Lock │a ⍺ │s ⌈ │d ⌊ │f _ │g ∇ │h ∆ │j ∘ │k ' │l ⎕ │; ⍎ │' ⍕ │ │
├────────┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──────────┤
│Shift │Z ⊆ │X │C │V │B │N │M │< ⍪ │> ⍙ │? ⍠ │Shift │
│ │z ⊂ │x ⊃ │c ∩ │v ∪ │b ⊥ │n ⊤ │m | │, ⍝ │. ⍀ │/ ⌿ │ │
└───────────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────────────┘
Additional charts for other layouts are available.
There are multiple ways to access the glyphs associated with a particular key.
Text editors
Keyboard layout extensions exist for several popular text editors like VS Code, Emacs and Vim. This is in addition to the availability of the below system-wide settings.
Shifting key
It is quite common to use Ctrl or Alt or AltGr (right-side Alt) as an additional shifting key. For example, AltGr+AltGr+4 would give ≤ while AltGr+Shift+4 would give ⍋.
- The Dyalog Unicode IME uses Ctrl
- NARS2000 uses Alt
- APLX uses AltGr with an option to also use Alt
for example, openSUSE 12.2, Ubuntu 12.10 and Fedora 17.
Prefix key
A prefix key is a special key or character which is entered immediately before typing the corresponding key.
- The Dyalog Unicode IME and the Dyalog RIDE (Remote Integrated Development Environment) uses ` by default, but allows choosing any key as prefix key.
- Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar recognises all the following as prefix keys: `, ½, ², ^,
º, §, ù, µ, °.

Android keyboard
- dzaima's Hacker's Keyboard + APL language using long-press to access APL glyphs.
Keyword look-up
- The Dyalog RIDE (Remote Integrated Development Environment) allows hitting the prefix key (` by default, but configurable) twice, followed by the (beginning of the) name of a symbol or a functionality. It then displays a drop-down of choices with arrow keys to indicate choice and the Tab key to insert the symbol. E.g. `,`,d,i,v,Tab↹ inserts
÷.
ASCII symbol combination
- Many APL glyphs can be approximated by overlaying or juxtaposing two ASCII characters. ngn/apl's scripted demo interface and Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar allow such a pair of characters and hitting the Tab key to replace them with the corresponding APL character. For example, <,-,Tab↹ will insert
←and T,o,Tab↹ will insert⍕.
On-screen language bar
Several APL IDEs allow the display of a toolbar with a button for each APL glyph:
- Dyalog APL, NARS2000, APL2 and ngn/apl's scripted demo interface all have this feature.
Web browsers
- Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar adds this to most web pages on demand.
| APL development [edit] | |
|---|---|
| Interface | Session ∙ Typing glyphs (on Linux) ∙ Fonts ∙ Text editors |
| Publications | Introductions ∙ Learning resources ∙ Simple examples ∙ Advanced examples ∙ Mnemonics ∙ ISO 8485:1989 ∙ ISO/IEC 13751:2001 ∙ A Dictionary of APL ∙ Case studies ∙ Documentation suites ∙ Books ∙ Papers ∙ Videos ∙ APL Quote Quad ∙ Vector journal ∙ Terminology (Chinese, German) ∙ Neural networks ∙ Error trapping with Dyalog APL (in forms) |
| Sharing code | Backwards compatibility ∙ APLcart ∙ APLTree ∙ APL-Cation ∙ Dfns workspace ∙ Tatin ∙ Cider |
| Implementation | Resources ∙ Open-source ∙ Magic function ∙ Performance ∙ APL hardware |
| Developers | Timeline of corporations ∙ APL2000 ∙ Dyalog ∙ IBM ∙ IPSA ∙ STSC |
| APL glyphs [edit] | |
|---|---|
| Information | Glyph ∙ Typing glyphs (on Linux) ∙ Unicode ∙ Fonts ∙ Mnemonics ∙ Overstrikes ∙ Migration level |
| Individual glyphs | Jot (∘) ∙ Right Shoe (⊃) ∙ Up Arrow (↑) ∙ Zilde (⍬) ∙ High minus (¯) ∙ Dot (.) ∙ Del (∇)
|
Hardware APL keyboard
A couple of hardware keyboards are being sold with APL symbols pre-printed onto the key caps:
- Dyalog sells US English, UK English, and Danish keyboards.
- Unicomp sells both entire keyboards and separate key caps for their keyboard range.