Typing glyphs: Difference between revisions
m (Reorder things) |
m (Remove lists category) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Hardware == | == Hardware == | ||
Once the keyboard map is configured to one's liking, it may be beneficial (especially for new users learning APL) to have a keyboard with APL symbols. There are a few solutions to this, such as purchasing a dedicated desktop keyboard | Once the keyboard map is configured to one's liking, it may be beneficial (especially for new users learning APL) to have a keyboard with APL symbols. There are a few solutions to this, such as purchasing a dedicated desktop keyboard, key caps for mechanical keyboards, or a keyboard decal. | ||
{| class=wikitable | |||
! Item !! Type !! Layout !! Languages !! Seller | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan=2 | Keyboard | |||
| [[wikipedia:Model_M_keyboard|Model M]] || [[Dyalog APL|Dyalog]] || 🇺🇸 || [https://www.amazon.com/Unicomp-Classic-Buckling-Spring-Keyboard/dp/B01M7V3M61/ref=sr_1_8 Amazon]. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Cherry (company)|Cherry]] || Dyalog || 🇺🇸 🇬🇧 🇩🇪 🇩🇰 || [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#mainContent Dyalog] | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan=4 | Key caps | |||
| Model M || Dyalog || 🇺🇸 ||[https://www.pckeyboard.com/page/product/USAPLSET Unicomp] | |||
|- | |||
| CannonKeys || [[APL2]] || 🇺🇸 || [https://cannonkeys.com/products/cannoncaps-big-blue?_pos=1&_sid=41ce0ba55&_ss=r cannonkeys.com] | |||
|- | |||
| Cherry || [[APL2]] || 🇺🇸 || [https://mykeyboard.eu/catalogue/pbt-crp-r4-alphas-apl_3957/ mykeyboard.eu] | |||
|- | |||
| Cherry || Dyalog || 🇺🇸 || [https://novelkeys.com/products/cherry-olivia?variant=43001363431591 NovelKeys] | |||
|- | |||
! Key stickers | |||
| any || Dyalog || 🇺🇸 || [https://www.tindie.com/products/russtopia/apl-keyboard-symbol-sticker-set/ Tindie] | |||
|} | |||
Note that these devices only are visual modifications on regular keyboards; they do not automatically enable entry of APL glyphs into software. For this, one of the below methods is required. | Note that these devices only are visual modifications on regular keyboards; they do not automatically enable entry of APL glyphs into software. For this, one of the below methods is required. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 34: | ||
=== Web === | === Web === | ||
[[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl in-browser language bar] adds APL keyboard functionality to most web pages on demand. | * [[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl in-browser language bar] adds APL keyboard functionality to most web pages on demand. | ||
[https://daveremba.com | * [https://daveremba.com/apl_vk_demo/ APL VK] is a virtual keyboard for the APL Language for modern mobile devices. You can add this to your own web page to provide a means to enter APL symbols into a web based form or editor. It is similar to the APL language bar but is optimized for mobile devices. | ||
You can add this to your own web page to provide a means to enter APL symbols into a web based form or editor. | |||
It is similar to the APL language bar but is optimized for mobile devices | |||
=== Text editors === | === Text editors === | ||
{{Main|Text editors}} | |||
Keyboard layout extensions exist for several popular | Keyboard layout extensions exist for several popular text editors like VS Code, Emacs and Vim. This can be an alternative, or complementary, to system-wide settings. | ||
=== Linux === | === Linux === | ||
{{Main|Typing glyphs on Linux}} | {{Main|Typing glyphs on Linux}} | ||
Most Linux distributions released after mid-2012 have Dyalog | * Most Linux distributions released after mid-2012 have Dyalog shifting-key support included with the distribution. | ||
* [https://github.com/secwang/espanso-apl-keyboard espanso-apl-keyboard] provides text replacement entry. | |||
[[File:Array Hacker's Keyboard.png|thumb|right|Array Hacker's Keyboard]] | [[File:Array Hacker's Keyboard.png|thumb|right|Array Hacker's Keyboard]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 61: | ||
* [[Adám Brudzewsky]] has [https://github.com/abrudz/Kbd various keyboard English layouts for Windows], which allow <kbd>AltGr</kbd> as shifting key, <kbd>`</kbd> as prefix key, or ASCII symbol composition. | * [[Adám Brudzewsky]] has [https://github.com/abrudz/Kbd various keyboard English layouts for Windows], which allow <kbd>AltGr</kbd> as shifting key, <kbd>`</kbd> as prefix key, or ASCII symbol composition. | ||
* | * [https://github.com/secwang/espanso-apl-keyboard espanso-apl-keyboard] provides text replacement entry. | ||
* The [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#tab-1 Dyalog Unicode IME] uses <kbd>Ctrl</kbd>. Unless unselected, this [[wikipedia:Input_method|IME]] is installed by default with [[Dyalog APL]]:<br>[[File:Dyalog_APL_Installer.png|frameless|Dyalog APL IME selected in installer]] | * The [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#tab-1 Dyalog Unicode IME] uses <kbd>Ctrl</kbd>. Unless unselected, this [[wikipedia:Input_method|IME]] is installed by default with [[Dyalog APL]]:<br>[[File:Dyalog_APL_Installer.png|frameless|Dyalog APL IME selected in installer]] | ||
* [https://github.com/Dyalog/APLAutoHotKey APLAutoHotKey] is an application to produce configurable AutoHotKey scripts for shifting key input. | |||
* e-sushi has [https://github.com/e-sushi/aplhotstrings/tree/main an AutoHotkey script] that allows ASCII composition. | |||
==== Troubleshooting ==== | ==== Troubleshooting ==== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 73: | ||
=== macOS === | === macOS === | ||
* [https://github.com/secwang/espanso-apl-keyboard espanso-apl-keyboard] provides text replacement entry. | |||
To enable these keyboard key mappings on [[wikipedia:macOS|macOS]], the appropriate <code>.keylayout</code> files for your locale must be downloaded and installed in the <code>/Library/Keyboard Layouts</code> directory: | To enable these keyboard key mappings on [[wikipedia:macOS|macOS]], the appropriate <code>.keylayout</code> files for your locale must be downloaded and installed in the <code>/Library/Keyboard Layouts</code> directory: | ||
* [[Dyalog Ltd.]] provides keyboard layouts for [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltDK.zip Danish], [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltIT.zip Finnish], [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltIT.zip Italian], [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltUK.zip British], and [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltUS.zip American]. | * [[Dyalog Ltd.]] provides keyboard layouts for [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltDK.zip Danish], [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltIT.zip Finnish], [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltIT.zip Italian], [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltUK.zip British], and [https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/files/download.php?file=DyalogAltUS.zip American]. | ||
* LdBeth provides a keyboard layout for [https://github.com/LdBeth/APL-JIS Japanese (JIS)]. | * LdBeth provides a keyboard layout for [https://github.com/LdBeth/APL-JIS Japanese (JIS)]. | ||
* [https://aplwiki.com/wiki/Typing_glyphs#ASCII_symbol_composition ASCII symbol composition] US and UK layouts are available from [https://github.com/abrudz/kbd#ascii-symbol-composition-layouts github.com/abrudz/kbd]. | * [https://aplwiki.com/wiki/Typing_glyphs#ASCII_symbol_composition ASCII symbol composition] US and UK layouts are available from [https://github.com/abrudz/kbd#ascii-symbol-composition-layouts github.com/abrudz/kbd]. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 86: | ||
* ohAitch's [https://github.com/ohAitch/APLiOS APLiOS], aimed primarily at iPadOS, provides a number bar and APL symbol layers. | * ohAitch's [https://github.com/ohAitch/APLiOS APLiOS], aimed primarily at iPadOS, provides a number bar and APL symbol layers. | ||
* [https://github.com/gitonthescene/APLKeyboard APLKeyboard] is built with [http://omz-software.com/pythonista/ Pythonista's] keyboard extension. The keys are a bit small but it's functional. | |||
== By method == | == By method == | ||
| Line 91: | Line 113: | ||
=== Shifting key === | === Shifting key === | ||
It is quite common to use <kbd>Ctrl</kbd> or <kbd>Alt</kbd> or <kbd>AltGr</kbd> (right-side <kbd>Alt</kbd>) as an additional shifting key. For example, <kbd>AltGr</kbd>+<kbd>4</kbd> would give < | It is quite common to use <kbd>Ctrl</kbd> or <kbd>Alt</kbd> or <kbd>AltGr</kbd> (right-side <kbd>Alt</kbd>) as an additional shifting key. For example, <kbd>AltGr</kbd>+<kbd>4</kbd> would give <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>≤</syntaxhighlight> while <kbd>AltGr</kbd>+<kbd>Shift</kbd>+<kbd>4</kbd> would give <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍋</syntaxhighlight>. | ||
* The [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#tab-1 Dyalog Unicode IME] uses <kbd>Ctrl</kbd> | * The [https://www.dyalog.com/apl-font-keyboard.htm#tab-1 Dyalog Unicode IME] uses <kbd>Ctrl</kbd> | ||
| Line 108: | Line 130: | ||
* [[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl in-browser language bar] recognises all the following as prefix keys: <kbd>`</kbd>, <kbd>½</kbd>, <kbd>²</kbd>, <kbd>^</kbd>, <kbd><s>º</s></kbd>, <kbd>§</kbd>, <kbd>ù</kbd>, <kbd>µ</kbd>, <kbd>°</kbd>. | * [[Adám Brudzewsky]]'s [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl in-browser language bar] recognises all the following as prefix keys: <kbd>`</kbd>, <kbd>½</kbd>, <kbd>²</kbd>, <kbd>^</kbd>, <kbd><s>º</s></kbd>, <kbd>§</kbd>, <kbd>ù</kbd>, <kbd>µ</kbd>, <kbd>°</kbd>. | ||
* Custom .XCompose files can be used on Linux as described in [https://aplwiki.com/wiki/Typing_glyphs_on_Linux#XCompose_(backtick/prefix/dead_key) the page Typing Glyphs on Linux]. | |||
[[File:RIDE keyword lookup.png|thumb|right|RIDE keyword lookup]] | [[File:RIDE keyword lookup.png|thumb|right|RIDE keyword lookup]] | ||
| Line 117: | Line 141: | ||
=== Keyword look-up === | === Keyword look-up === | ||
The [https://github.com/Dyalog/ride/releases/latest Dyalog RIDE] (Remote Integrated Development Environment) allows hitting the prefix key (<kbd>`</kbd> by default, but configurable) twice, followed by the (beginning of the) name of a symbol or a functionality. It then displays a drop-down of choices with arrow keys to indicate choice and the Tab key to insert the symbol. E.g. <kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>d</kbd>,<kbd>i</kbd>,<kbd>v</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> inserts <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>÷</syntaxhighlight>. | |||
=== ASCII symbol composition === | === ASCII symbol composition === | ||
Many APL glyphs can be approximated by overlaying or juxtaposing two ASCII characters. [[ngn/apl]]'s scripted demo interface, [https://abrudz.github.io/lb/apl Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar], and [[TryAPL]]'s web interface allow such a pair of characters and hitting the <kbd>Tab↹</kbd> key to replace them with the corresponding APL character. For example, <kbd><</kbd>,<kbd>-</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> will insert <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>←</syntaxhighlight> and <kbd>T</kbd>,<kbd>o</kbd>,<kbd>Tab↹</kbd> will insert <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⍕</syntaxhighlight>. | |||
For Windows users, e-sushi has [https://github.com/e-sushi/aplhotstrings/tree/main an AutoHotkey script] that allows such composition. | |||
=== Text replacement === | |||
[https://github.com/espanso/espanso Espanso] allows typing a pattern which is then immediately replaced with something else. This can be used in various ways to type APL glyphs without conflicting with application or operating system keyboard shortcuts. [https://github.com/secwang/espanso-apl-keyboard espanso-apl-keyboard] is an Espanso configuration that emulates prefix key, so for example typing pressing <kbd>`</kbd>,<kbd>e</kbd> too type <code>`e</code> will be end up producing the <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>∊</syntaxhighlight> glyph. | |||
[[File:NARS2000 language bar.png|thumb|right|NARS2000 language bar]] | [[File:NARS2000 language bar.png|thumb|right|NARS2000 language bar]] | ||
| Line 138: | Line 168: | ||
To check your setup is fully functional you can try compiling the following template: | To check your setup is fully functional you can try compiling the following template: | ||
[[File:LaTeX APL template.png|thumb|right|Screenshot of the typeset document]] | [[File:LaTeX APL template.png|thumb|right|Screenshot of the typeset document]] | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=latex> | ||
\documentclass[11pt]{article} | \documentclass[11pt]{article} | ||
| Line 152: | Line 182: | ||
\end{document} | \end{document} | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Depending on whether you want the whole document to use the APL font or not, you may remove the command to set the main font. If you do so, APL glyphs will be rendered correctly inside code listings and similar environments, but not in the main body of the document. | Depending on whether you want the whole document to use the APL font or not, you may remove the command to set the main font. If you do so, APL glyphs will be rendered correctly inside code listings and similar environments, but not in the main body of the document. | ||
==== Listings ==== | ==== Listings ==== | ||
LuaLaTeX and XeLaTeX can use the [https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/LaTeX/Source_Code_Listings ''listings'' package] to include APL source with the following document preamble:<ref>Baker, John D. [https://analyzethedatanotthedrivel.org/2011/08/15/typesetting-utf8-apl-code-with-the-latex-lstlisting-package/ Typesetting UTF8 APL code with the LaTeX lstlisting package]. Analyze the Data not the Drivel. August 15, 2011.</ref> | LuaLaTeX and XeLaTeX can use the [https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/LaTeX/Source_Code_Listings ''listings'' package] to include APL source with the following document preamble:<ref>Baker, John D. [https://analyzethedatanotthedrivel.org/2011/08/15/typesetting-utf8-apl-code-with-the-latex-lstlisting-package/ Typesetting UTF8 APL code with the LaTeX lstlisting package]. Analyze the Data not the Drivel. August 15, 2011.</ref> | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=latex> | ||
% set lstlisting to accept UTF8 APL text | % set lstlisting to accept UTF8 APL text | ||
\makeatletter | \makeatletter | ||
| Line 186: | Line 216: | ||
\lst@RestoreCatcodes | \lst@RestoreCatcodes | ||
\makeatother | \makeatother | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== Metafont ==== | |||
An APL metafont usable to typeset APL in LaTeX files is available on the ([https://ctan.org/pkg/apl?lang=en Comprehensive TeX Archive Network]), available for free use. | |||
The version of the package is from 1987 and may not be suitable for glyphs used in modern APL implementations.. | |||
=== plainTeX === | === plainTeX === | ||
| Line 193: | Line 228: | ||
[[File:3270 APL font sample.png|thumb|right|Screenshot of the typeset document]] | [[File:3270 APL font sample.png|thumb|right|Screenshot of the typeset document]] | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang=latex> | ||
\input apldef.tex | \input apldef.tex | ||
| Line 217: | Line 252: | ||
\DL | \DL | ||
\bye | \bye | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 223: | Line 258: | ||
{{APL development}} | {{APL development}} | ||
{{APL glyphs}} | {{APL glyphs}} | ||
[[Category:APL character set | [[Category:APL character set]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 6 August 2024
APL uses a range of special graphic symbols to represent most functions and operators. While keyboard mappings become memorized over time, entering APL characters can frustrate the beginner. However, a study involving high school students found that typing and using APL characters did not hinder the students in any measurable way. There are several convenient ways to enter the glyphs.

Hardware
Once the keyboard map is configured to one's liking, it may be beneficial (especially for new users learning APL) to have a keyboard with APL symbols. There are a few solutions to this, such as purchasing a dedicated desktop keyboard, key caps for mechanical keyboards, or a keyboard decal.
| Item | Type | Layout | Languages | Seller |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyboard | Model M | Dyalog | 🇺🇸 | Amazon. |
| Cherry | Dyalog | 🇺🇸 🇬🇧 🇩🇪 🇩🇰 | Dyalog | |
| Key caps | Model M | Dyalog | 🇺🇸 | Unicomp |
| CannonKeys | APL2 | 🇺🇸 | cannonkeys.com | |
| Cherry | APL2 | 🇺🇸 | mykeyboard.eu | |
| Cherry | Dyalog | 🇺🇸 | NovelKeys | |
| Key stickers | any | Dyalog | 🇺🇸 | Tindie |
Note that these devices only are visual modifications on regular keyboards; they do not automatically enable entry of APL glyphs into software. For this, one of the below methods is required.
By platform
Web
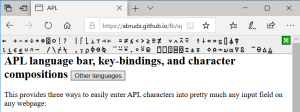
- Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar adds APL keyboard functionality to most web pages on demand.
- APL VK is a virtual keyboard for the APL Language for modern mobile devices. You can add this to your own web page to provide a means to enter APL symbols into a web based form or editor. It is similar to the APL language bar but is optimized for mobile devices.
Text editors
- Main article: Text editors
Keyboard layout extensions exist for several popular text editors like VS Code, Emacs and Vim. This can be an alternative, or complementary, to system-wide settings.
Linux
- Main article: Typing glyphs on Linux
- Most Linux distributions released after mid-2012 have Dyalog shifting-key support included with the distribution.
- espanso-apl-keyboard provides text replacement entry.
Android
- dzaima's Array Hacker's Keyboard uses a long-press to access APL glyphs.
- Optima Systems' APL Keys provides both QWERTY keyboard (which uses long-press to select from a list of alternate glyphs), a phone pad, and a symbol view.
Windows
- Adám Brudzewsky has various keyboard English layouts for Windows, which allow AltGr as shifting key, ` as prefix key, or ASCII symbol composition.
- espanso-apl-keyboard provides text replacement entry.
- The Dyalog Unicode IME uses Ctrl. Unless unselected, this IME is installed by default with Dyalog APL:
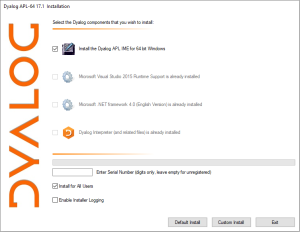
- APLAutoHotKey is an application to produce configurable AutoHotKey scripts for shifting key input.
- e-sushi has an AutoHotkey script that allows ASCII composition.
Troubleshooting
Installation of the Dyalog Unicode IME can cause so many layouts to be installed that they get in the way when switching layouts. However, the unneeded layouts can be removed through editing the registry[1]
macOS
- espanso-apl-keyboard provides text replacement entry.
To enable these keyboard key mappings on macOS, the appropriate .keylayout files for your locale must be downloaded and installed in the /Library/Keyboard Layouts directory:
- LdBeth provides a keyboard layout for Japanese (JIS).
- ASCII symbol composition US and UK layouts are available from github.com/abrudz/kbd.
iOS
- ohAitch's APLiOS, aimed primarily at iPadOS, provides a number bar and APL symbol layers.
- APLKeyboard is built with Pythonista's keyboard extension. The keys are a bit small but it's functional.
By method
Most of today's APLs use a mapping which derives from the original APL\360 terminals' keyboard layout. For example, Dyalog APL's standard US English layout for is as follows:
┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬─────────┐
│~ ⌺ │! ⌶ │@ ⍫ │# ⍒ │$ ⍋ │% ⌽ │^ ⍉ │& ⊖ │* ⍟ │( ⍱ │) ⍲ │_ ! │+ ⌹ │Backspace│
│` ⋄ │1 ¨ │2 ¯ │3 < │4 ≤ │5 = │6 ≥ │7 > │8 ≠ │9 ∨ │0 ∧ │- × │= ÷ │ │
├────┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬──────┤
│Tab │Q │W │E ⍷ │R │T ⍨ │Y │U │I ⍸ │O ⍥ │P ⍣ │{ ⍞ │} ⍬ │| ⊣ │
│ │q ? │w ⍵ │e ∊ │r ⍴ │t ~ │y ↑ │u ↓ │i ⍳ │o ○ │p * │[ ← │] → │\ ⊢ │
├───────┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴┬───┴──────┤
│Caps │A │S │D │F │G │H │J ⍤ │K ⌸ │L ⌷ │: ≡ │" ≢ │Enter │
│Lock │a ⍺ │s ⌈ │d ⌊ │f _ │g ∇ │h ∆ │j ∘ │k ' │l ⎕ │; ⍎ │' ⍕ │ │
├────────┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──┬─┴──────────┤
│Shift │Z ⊆ │X │C │V │B │N │M │< ⍪ │> ⍙ │? ⍠ │Shift │
│ │z ⊂ │x ⊃ │c ∩ │v ∪ │b ⊥ │n ⊤ │m | │, ⍝ │. ⍀ │/ ⌿ │ │
└───────────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────────────┘
Additional charts for other layouts are available.
There are multiple ways to access the glyphs associated with a particular key.
Shifting key
It is quite common to use Ctrl or Alt or AltGr (right-side Alt) as an additional shifting key. For example, AltGr+4 would give ≤ while AltGr+Shift+4 would give ⍋.
- The Dyalog Unicode IME uses Ctrl
- NARS2000 uses Alt
- APLX uses AltGr with an option to also use Alt
Prefix key
A prefix key is a special key or character which is entered immediately before typing the corresponding key.
- The Dyalog Unicode IME and the Dyalog RIDE (Remote Integrated Development Environment) uses ` by default, but allows choosing any key as prefix key.
- Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar recognises all the following as prefix keys: `, ½, ², ^,
º, §, ù, µ, °.
- Custom .XCompose files can be used on Linux as described in the page Typing Glyphs on Linux.
Long-press
dzaima's Hacker's Keyboard + APL language reacts to a long-press, popping up a palette that allows selecting any of the APL glyphs associated with that button.
Keyword look-up
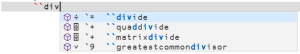
The Dyalog RIDE (Remote Integrated Development Environment) allows hitting the prefix key (` by default, but configurable) twice, followed by the (beginning of the) name of a symbol or a functionality. It then displays a drop-down of choices with arrow keys to indicate choice and the Tab key to insert the symbol. E.g. `,`,d,i,v,Tab↹ inserts ÷.
ASCII symbol composition
Many APL glyphs can be approximated by overlaying or juxtaposing two ASCII characters. ngn/apl's scripted demo interface, Adám Brudzewsky's in-browser language bar, and TryAPL's web interface allow such a pair of characters and hitting the Tab↹ key to replace them with the corresponding APL character. For example, <,-,Tab↹ will insert ← and T,o,Tab↹ will insert ⍕.
For Windows users, e-sushi has an AutoHotkey script that allows such composition.
Text replacement
Espanso allows typing a pattern which is then immediately replaced with something else. This can be used in various ways to type APL glyphs without conflicting with application or operating system keyboard shortcuts. espanso-apl-keyboard is an Espanso configuration that emulates prefix key, so for example typing pressing `,e too type `e will be end up producing the ∊ glyph.
On-screen language bar
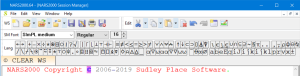
Several APL IDEs allow the display of a toolbar with a button for each APL glyph:
- Dyalog APL, NARS2000, APL2 and ngn/apl's scripted demo interface all have this feature.
LaTeX
In order to typeset APL using LaTeX, you need to be sure your LaTeX engine has full Unicode support. At the time of writing, LuaLaTeX and XeLaTeX are two of the most popular such alternatives, both included with TeX Live.
After ensuring you have a LaTeX engine that is Unicode capable, you need to make sure your .tex document is using a font that has the APL glyphs you want to type. One way to do this is through the fontspec package, as seen in the example template below.
To check your setup is fully functional you can try compiling the following template:
\documentclass[11pt]{article}
\usepackage{fontspec}
\setmainfont{APL385 Unicode}
\setmonofont{APL385 Unicode}[Scale=MatchLowercase]
\begin{document}
I just want some ← +-×÷*⍟⌹○!? |⌈⌊⊥⊤⊣⊢ =≠≤<>≥≡≢ ∨∧⍲⍱ ↑↓⊂⊃⊆⌷⍋⍒ ⍳⍸∊⍷∪∩~ /\textbackslash⌿⍀ ,⍪⍴⌽⊖⍉ ¨⍨⍣.∘⍤⍥@ ⍞⎕⍠⌸⌺⌶⍎⍕ ⋄⍝→⍵⍺∇\& ¯⍬
\texttt{The ``setmonofont'' was needed because of this, otherwise ⍺⌊¯→⍬ wouldn't show properly}.
\end{document}
Depending on whether you want the whole document to use the APL font or not, you may remove the command to set the main font. If you do so, APL glyphs will be rendered correctly inside code listings and similar environments, but not in the main body of the document.
Listings
LuaLaTeX and XeLaTeX can use the listings package to include APL source with the following document preamble:[2]
% set lstlisting to accept UTF8 APL text
\makeatletter
\lst@InputCatcodes
\def\lst@DefEC{%
\lst@CCECUse \lst@ProcessLetter
^^80^^81^^82^^83^^84^^85^^86^^87^^88^^89^^8a^^8b^^8c^^8d^^8e^^8f%
^^90^^91^^92^^93^^94^^95^^96^^97^^98^^99^^9a^^9b^^9c^^9d^^9e^^9f%
^^a0^^a1^^a2^^a3^^a4^^a5^^a6^^a7^^a8^^a9^^aa^^ab^^ac^^ad^^ae^^af%
^^b0^^b1^^b2^^b3^^b4^^b5^^b6^^b7^^b8^^b9^^ba^^bb^^bc^^bd^^be^^bf%
^^c0^^c1^^c2^^c3^^c4^^c5^^c6^^c7^^c8^^c9^^ca^^cb^^cc^^cd^^ce^^cf%
^^d0^^d1^^d2^^d3^^d4^^d5^^d6^^d7^^d8^^d9^^da^^db^^dc^^dd^^de^^df%
^^e0^^e1^^e2^^e3^^e4^^e5^^e6^^e7^^e8^^e9^^ea^^eb^^ec^^ed^^ee^^ef%
^^f0^^f1^^f2^^f3^^f4^^f5^^f6^^f7^^f8^^f9^^fa^^fb^^fc^^fd^^fe^^ff%
^^^^20ac^^^^0153^^^^0152%
^^^^20a7^^^^2190^^^^2191^^^^2192^^^^2193^^^^2206^^^^2207^^^^220a%
^^^^2218^^^^2228^^^^2229^^^^222a^^^^2235^^^^223c^^^^2260^^^^2261%
^^^^2262^^^^2264^^^^2265^^^^2282^^^^2283^^^^2296^^^^22a2^^^^22a3%
^^^^22a4^^^^22a5^^^^22c4^^^^2308^^^^230a^^^^2336^^^^2337^^^^2339%
^^^^233b^^^^233d^^^^233f^^^^2340^^^^2342^^^^2347^^^^2348^^^^2349%
^^^^234b^^^^234e^^^^2350^^^^2352^^^^2355^^^^2357^^^^2359^^^^235d%
^^^^235e^^^^235f^^^^2361^^^^2362^^^^2363^^^^2364^^^^2365^^^^2368%
^^^^236a^^^^236b^^^^236c^^^^2371^^^^2372^^^^2373^^^^2374^^^^2375%
^^^^2377^^^^2378^^^^237a^^^^2395^^^^25af^^^^25ca^^^^25cb%
^^00}
\lst@RestoreCatcodes
\makeatother
Metafont
An APL metafont usable to typeset APL in LaTeX files is available on the (Comprehensive TeX Archive Network), available for free use. The version of the package is from 1987 and may not be suitable for glyphs used in modern APL implementations..
plainTeX
LdBeth has made a Type1 version of 3270 font with APL support, suitable for traditional TeX implementations that cannot directly use TTF/OTF fonts.
\input apldef.tex
\font\apl=3270
\apl
1234567890{\rm Good?}\NG1+2-3{\rm Mixing some roman}
I just want some \IS +-\ML\DV\ST\LG\DQ\LO{}!?\ |\CE\FL\DE\EN\LK\RK\ =\NE\LE<>\GE\EU\SE
\AD\OR\NA\NO\ \UA\DA\RU\LU\SS\SQ\GU\GD\ \IO\UI\EP\UE\UU\DU\NT\ /\BL\CS\CB\ ,\BC\RO\RV\CR\TR
\DD\RR\PP.\SO\RN\OV{}@\ \QQ\BX\CQ\EQ\MQ\IB\XQ\FM\ \DM\LM\GO\OM\AM\DL\&
\NG\NL
\obeylines\DL S\IS SUM N;I
S\IS I\IS 0
\GO (N<I\IS I+1)/0
S\IS S+I\ST 2
\GO 2
\DL
\bye
References
- ↑ Chan, Vince. How to remove Dyalog APL IME from various languages (MS WIN). Dyalog Forums. November 3, 2021.
- ↑ Baker, John D. Typesetting UTF8 APL code with the LaTeX lstlisting package. Analyze the Data not the Drivel. August 15, 2011.
| APL development [edit] | |
|---|---|
| Interface | Session ∙ Typing glyphs (on Linux) ∙ Fonts ∙ Text editors |
| Publications | Introductions ∙ Learning resources ∙ Simple examples ∙ Advanced examples ∙ Mnemonics ∙ ISO 8485:1989 ∙ ISO/IEC 13751:2001 ∙ A Dictionary of APL ∙ Case studies ∙ Documentation suites ∙ Books ∙ Papers ∙ Videos ∙ APL Quote Quad ∙ Vector journal ∙ Terminology (Chinese, German) ∙ Neural networks ∙ Error trapping with Dyalog APL (in forms) |
| Sharing code | Backwards compatibility ∙ APLcart ∙ APLTree ∙ APL-Cation ∙ Dfns workspace ∙ Tatin ∙ Cider |
| Implementation | Resources ∙ Open-source ∙ Magic function ∙ Performance ∙ APL hardware |
| Developers | Timeline of corporations ∙ APL2000 ∙ Dyalog ∙ IBM ∙ IPSA ∙ STSC |
| APL glyphs [edit] | |
|---|---|
| Information | Glyph ∙ Typing glyphs (on Linux) ∙ Unicode ∙ Fonts ∙ Mnemonics ∙ Overstrikes ∙ Migration level |
| Individual glyphs | Jot (∘) ∙ Right Shoe (⊃) ∙ Up Arrow (↑) ∙ Zilde (⍬) ∙ High minus (¯) ∙ Dot (.) ∙ Del (∇)
|