Array notation: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "'''Array notation''' is a way to write most arrays literally, with no or minimal use of primitive functions, possibly over multiple code lines. While APL has had at le...") |
m (APLAN abbreviation) |
||
| (61 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | {{Built-ins|Array notation|(⋄)|[⋄]}}, abbreviated '''APLAN''' parallel to [[wikipedia:JSON|JSON]], is a way to write most [[array]]s literally, with no or minimal use of [[primitive function]]s, possibly over multiple code lines. It differs from the [[strand notation]] existing since [[APL\360]] in that it can be used to write arrays of rank greater than one. Array notation is supported in [[dzaima/APL]], [[BQN]] (using angle brackets <code>⟨⋄⟩</code> instead of round parentheses <code>(⋄)</code>), and some tools for [[Dyalog APL]], where it is planned as an eventual language feature. | ||
Array notation generally consists of a vector notation written with parentheses <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>()</syntaxhighlight>, roughly equivalent to stranding, and a high-rank notation using square brackets <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>[]</syntaxhighlight>, indicating the [[Mix]] of a vector. It also supports [[namespace]]s, using <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>name:value</syntaxhighlight> syntax in round parentheses. [[Statement separator]]s must appear between elements and between [[wikipedia:name–value_pair|name–value pair]]s. | |||
== Examples == | |||
Medium-sized array constants are often needed in code. Due to the lack of a native multi-line notation, programmers have resorted to various ad-hoc methods of approximating such, usually at the cost of reduced [[readability]]. A very common technique is repeated [[concatenate|concatenation]] resulting in the desired value being held in a variable (<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>z</syntaxhighlight> in the below examples), as opposed to array notation which can express the final value directly. In addition, the traditional technique sometimes involves the creation of helper variables as a side effect. | |||
=== Basic arrays === | |||
{| class=wikitable | |||
! Traditional method !! Array notation !! Description | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(0 6 1 8)(1 4 1 4 2)(2 7 1 8 2 8)(3 1 4 1 5)</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(0 6 1 8 ⋄ 1 4 1 4 2 ⋄ 2 7 1 8 2 8 ⋄ 3 1 4 1 5)</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Vector of numeric vectors on a single line. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z← (0 6 1 8)(1 4 1 4 2) | |||
z,←(2 7 1 8 2 8)(3 1 4 1 5)</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(0 6 1 8 ⋄ 1 4 1 4 2 | |||
2 7 1 8 2 8 ⋄ 3 1 4 1 5)</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Vector of numeric vectors split over two lines. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←,⊂'Three' | |||
z,←⊂'Blind' | |||
z,←⊂'Mice'</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>('Three' | |||
'Blind' | |||
'Mice')</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Vector of character vectors, one on each line. (The traditional method includes an unnecessary <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>,</syntaxhighlight> to indicate that <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>z</syntaxhighlight> will be a vector.) | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⍉⍪0 6 1 8 | |||
z⍪← 1 4 1 4 | |||
z⍪← 2 7 1 8 | |||
z⍪← 3 1 4 2</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>[0 6 1 8 | |||
1 4 1 4 | |||
2 7 1 8 | |||
3 1 4 2]</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Numeric matrix. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⍪10 | |||
z⍪←20 | |||
z⍪←30 | |||
z⍪←40</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>[10 | |||
20 | |||
30 | |||
40]</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Column matrix. | |||
|} | |||
=== Involved arrays === | |||
{| class=wikitable | |||
! Traditional method !! Array notation !! Description | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>a←⍉⍪0 0 1 | |||
a⍪← 1 0 1 | |||
a⍪← 0 1 1 | |||
z←,⊂a | |||
a←⍉⍪0 1 1 | |||
a⍪← 1 1 0 | |||
a⍪← 0 1 0 | |||
z,←⊂a | |||
a←⍉⍪0 1 1 1 | |||
a⍪← 1 1 1 0 | |||
z,←⊂a | |||
a←⍉⍪0 1 1 0 | |||
a⍪← 1 0 0 1 | |||
a⍪← 0 1 1 0 | |||
z,←⊂a</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>([0 0 1 | |||
1 0 1 | |||
0 1 1] | |||
[0 1 1 | |||
1 1 0 | |||
0 1 0] | |||
[0 1 1 1 | |||
1 1 1 0] | |||
[0 1 1 0 | |||
1 0 0 1 | |||
0 1 1 0])</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Vector of matrices. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⍉⍪0 'OK' | |||
z⍪← 1 'WS FULL' | |||
z⍪← 2 'SYNTAX ERROR' | |||
z⍪← 3 'INDEX ERROR' | |||
z⍪← 4 'RANK ERROR'</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>[0 'OK' | |||
1 'WS FULL' | |||
2 'SYNTAX ERROR' | |||
3 'INDEX ERROR' | |||
4 'RANK ERROR']</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Table with numeric and text columns. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>a←⍉⍪3 1 4 | |||
a⍪← 1 5 0 | |||
a←↑a | |||
b←⍉⍪2 7 0 | |||
b⍪← 2 0 0 | |||
z←a,[0.5] b</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>[[3 1 4 | |||
1 5 0] | |||
[2 7 0 | |||
2 0 0]]</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Rank 3 numeric array. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>a←,⊂3 1 4 | |||
a,←⊂1 5 | |||
a←↑a | |||
b←,⊂2 7 | |||
b,← 2 | |||
b←↑b | |||
z←↑a b</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>[[3 | |||
1 5 9] | |||
[2 7 | |||
2]]</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Rank 3 numeric array relying on automatic padding with [[fill element]]. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | |||
z←⍉⍪'fns' ((0 1)(0.7 0)(0.7 0)×size) | |||
z⍪← 'fnd' ((0 1)(0 0)(0 0)×size) | |||
z⍪← 'lines'((0 0)(0.7 0)(0.7 0)×size) | |||
z⍪← 'lnd' ((0 0)(0 0)(0 0)×size) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl> | |||
['fns' ((0 1 ⋄ 0.7 0 ⋄ 0.7 0)×size) | |||
'fnd' ((0 1 ⋄ 0 0 ⋄ 0 0)×size) | |||
'lines'((0 0 ⋄ 0.7 0 ⋄ 0.7 0)×size) | |||
'lnd' ((0 0 ⋄ 0 0 ⋄ 0 0)×size)] | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Matrix of simple and nested vectors, with dynamic values. | |||
|} | |||
=== Namespaces === | |||
{| class=wikitable | |||
! Traditional method !! Array notation !! Description | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>⎕NS⍬</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>()</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Empty namespace. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>⎕NS¨⍬⍬⍬</syntaxhighlight>or<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(⎕NS⍬)(⎕NS⍬)(⎕NS⍬)</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>()()()</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Vector of namespaces. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⎕NS⍬ | |||
z.x←'hello'</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(x:'hello')</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Namespace with character vector member. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⎕NS⍬ | |||
z.x←⍉⍪'hello' | |||
z.x⍪← 'world'</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(x:['hello' | |||
'world'])</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Namespace with character matrix member. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⎕NS⍬ | |||
z.y←⎕NS⍬ | |||
z.y.x←⍉⍪'hello' | |||
z.y.x⍪← 'world'</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>(y:(x:['hello' | |||
'world']))</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|Nested namespace structure with matrix member. | |||
|- | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>z←⎕NS⍬ | |||
z.f←+ | |||
a←⎕NS⍬ | |||
a.f←- | |||
z,←a | |||
a←⎕NS⍬ | |||
a.f←× | |||
z,←a | |||
a←⎕NS⍬ | |||
a.f←÷ | |||
z←z.f</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|<syntaxhighlight lang=apl>((f:+)(f:-)(f:×)(f:÷)).f</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|[[Function array]]. | |||
|} | |||
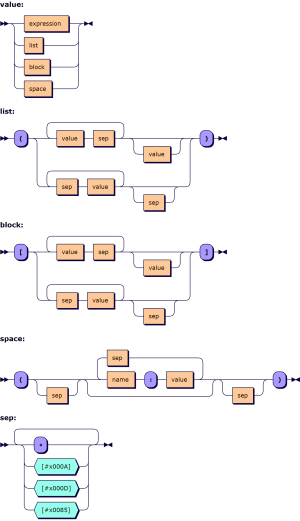
[[File:Array notation syntax.png|thumb|right|[[wikipedia:Railroad diagram|Railroad diagram]].]] | |||
== Specification == | |||
The notation consists of syntax that was invalid before its introduction, thus causing no issues for [[backwards compatibility]]. The added syntax consists of three constructs that are currently [[SYNTAX ERROR]]s: | |||
* ''broken'' round parentheses: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>(</syntaxhighlight>…<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>)</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* ''broken'' square brackets: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>[</syntaxhighlight>…<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>]</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* empty round parentheses: <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>()</syntaxhighlight> | |||
where ''broken'' means interrupted by one or more [[diamond]]s (<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>⋄</syntaxhighlight>) or line breaks (outside of [[dfn]]s). | |||
* A ''broken'' round parenthesis creates a [[namespace]] if every diamond/line break-separated statement is a ''name-value pair''. | |||
* A ''broken'' round parenthesis creates a [[vector]] if every diamond/line break-separated statement is a value expression. In that case, every such statement forms an [[element]] in the resulting vector. | |||
* <span id=minrank1>A ''broken'' square bracket creates a an [[array]] where every diamond/line break-separated statement forms a [[major cell]] in the resulting array.[[#minrank1note|*]]<span> | |||
* <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>()</syntaxhighlight> creates a new namespace — equivalent to <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>(⎕NS 0⍴⊂'')</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* A ''name-value pair'' consists of a valid APL identifier, followed by a colon (<syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>:</syntaxhighlight>) and a value expression. | |||
<span id=minrank1note>[[#minrank1|*]]</span> This rule is followed strictly in [[dzaima/APL]], while [[Dyalog APL]] considers each statement to have a rank of at least 1, even if it is a [[scalar]]. | |||
=== Formal syntax === | |||
The array notation can be described using [[wikipedia:Extended Backus–Naur form|Extended Backus–Naur form]], where an <code>expression</code> is any traditional APL expression: | |||
<pre> | |||
value ::= expression | list | block | space | |||
list ::= '(' ( ( value sep )+ value? | ( sep value )+ sep? ) ')' | |||
block ::= '[' ( ( value sep )+ value? | ( sep value )+ sep? ) ']' | |||
space ::= '(' sep? ( name ':' value ( sep name ':' value )* )? sep? ')' | |||
sep ::= [⋄#x000A#x000D#x0085]+ | |||
</pre> | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
[[ | :''See also the [[Array notation design considerations#Timeline]]'' | ||
One-dimensional list syntax with surrounding brackets and delimiters, matching [[wikipedia:sequence|sequence]] notation in mathematics, is common in programming. It appears as early as [[wikipedia:ALGOL 68|ALGOL 68]] with parentheses, and square-bracket lists feature in languages from the 1970s such as [[wikipedia:ML (programming language)|ML]] and [[wikipedia:Icon (programming language)|Icon]]. [[MATLAB]] uses matrix syntax with square brackets, semicolons to separate rows, and commas to separate elements within a row. [[wikipedia:FP (programming language)|FP]] uses angle brackets for lists, and square brackets for function "construction", with behavior like [[function array]]s. | |||
List notation appears in [[Nial]] using brackets and commas like <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>[a,b,c]</syntaxhighlight>, and allowing function arrays called "atlases". [[A+]] and [[K]] have a list notation using parentheses and semicolons like <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>(a;b;c)</syntaxhighlight>. In A+ this is related to [[bracket indexing]] and an "expression group" notation written with curly braces and semicolons. It allows line breaks, but in addition to rather than in place of semicolons. The later K version corresponds more closely to APL: the semicolon is a statement separator and is interchangeable with a line break, and because K represents arrays with nested lists, it corresponds to both vector and high-rank array notation. | |||
[[ | The first published proposals that influenced [[Dyalog APL]]'s array notation were made by [[Phil Last]] at [[Dyalog '15]] and later in [[Vector Journal]].<ref>[[Phil Last]]. [https://dyalog.tv/Dyalog15/?v=9-HAvTMhYao APL Array Notation] ([https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/conference/dyalog15/presentations/U07_APL_Array_Notation.pdf transcript]). [[Dyalog '15]].</ref><ref>[[Phil Last]]. [http://archive.vector.org.uk/art10501450 A Notation for APL array Embedding and Serialization]. [[Vector Journal]], Volume 26, number 4. [[British APL Association]]. 2016.</ref> Last cited the syntax of [[dfn]]s as a sequence of expressions with enclosing braces, as well as [[APL#]]'s namespace notation enclosed in double brackets <code>[[]]</code>, as precursors. He also used the design in Acre Desktop, a project manager for Dyalog APL, to support storing constant arrays and namespaces in text files. Following the conference presentation, [[Adám Brudzewsky]] began work on array notation and presented on it in a series of conferences, initially using parentheses for the high-rank notation<ref>[[Adám Brudzewsky]]. [https://dyalog.tv/Dyalog17/?v=CRQNzL8cUQE Literal Notation for Arrays and Namespaces] ([https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/conference/dyalog17/presentations/D11_Literal_Notation_for_Arrays_and_Namespaces.pdf slides]). [[Dyalog '17]].</ref> and later returning to square brackets.<ref>[[Adám Brudzewsky]]. [https://dyalog.tv/Dyalog18/?v=GAdQuOtPcfM Array Notation Mk III]. [[Dyalog '18]].</ref><ref>[[Adám Brudzewsky]]. [https://apl-germany.de/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/APL_Journal_2020_1u2.pdf#page=34 A Notation for APL Arrays]. APL-Journal, Volume 2020, number 1-2. [[APL Germany|APL-Germany e.V.]] 2020.</ref> Because Last's use of <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>←</syntaxhighlight> to separate namespace keys from values prevented lists from including arbitrary expressions (which might contain assignment), he proposed a change to <syntaxhighlight lang=apl inline>:</syntaxhighlight> as in [[wikipedia:JSON|JSON]]. [[Dyalog APL 18.0]], released in 2020, included support for array notation in source files loaded by Link<ref>[[Dyalog Ltd]]. [https://dyalog.github.io/link/3.0/Discussion/TechDetails/#creating-apl-source-files-and-directories Link User Guide: Creating APL Source Files and Directories]. Retrieved 2022-08-24.</ref>, but not in the language itself.<ref>[[Adám Brudzewsky]]. [https://dyalog.tv/Dyalog20/?v=5drncJiWOM4 Array Notation RC1] ([https://www.dyalog.com/uploads/conference/dyalog20/presentations/D09_Array_Notation_RC1.pdf slides]). [[Dyalog '20]].</ref> | ||
= | |||
The project manager Acre Desktop added support for the non-namespace parts of the notation in early 2018, together with Phil Last's original namespace notation, using square brackets and assignment arrow. [[dzaima/APL]] added support for vector notation with parentheses in 2018, namespaces and function arrays in 2019, and high-rank arrays with square brackets in 2020. [[BQN]] supported lists with angle brackets (<code>⟨</code>…<code>⟩</code>) in its initial implementation in 2020; square brackets (<code>[</code>…<code>]</code>) were reserved for high-rank array notation, which was implemented in 2022. | |||
On April 21, 2023, Dyalog Ltd published a blog post by Morten Kromberg announcing to the [[community]] the formal proposal for an APL array notation<ref name=formprop>Kromberg, Morten. [https://www.dyalog.com/blog/2023/04/formal-proposal-for-apl-array-notation-seeking-feedback/ Formal Proposal for APL Array Notation – Seeking Feedback]. Formal Proposal for APL Array Notation – Seeking Feedback. April 21, 2023.</ref> and by May 5, the specification for scoping in namespaces was changed due to feedback from Dyalog Ltd employee Peter Mikkelsen: Assignments inside value expressions would now affect the surrounding scope rather than having [[dfn]]-like auto-localisation, which can instead be achieved by wrapping the expression in an anonymous dfn. | |||
{{Template:Comparison of array notations}} | |||
== Documentation == | |||
* [https://mlochbaum.github.io/BQN/doc/arrayrepr.html#array-literals BQN] (as <code>⟨⋄⟩</code>, <code>[⋄]</code>, and <code>{key⇐val⋄}</code>) | |||
* [https://www.nial-array-language.org/ndocs/NialDict2.html#bracket-comma-notation Nial] (as <code>[,]</code> for vectors) | |||
== External links == | |||
* [https://abrudz.github.io/aplan/Formal%20Proposal%20%E2%80%94%20APL%20Array%20Notation.pdf Formal Proposal] document | |||
* [https://abrudz.github.io/aplan Evaluate APL Array Notation] sandbox | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
{{APL syntax}}[[Category:APL syntax]][[Category:Nested array model]] | {{APL syntax}}[[Category:APL syntax]][[Category:Nested array model]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:23, 21 September 2023
(⋄) [⋄]
|
Array notation ((⋄), [⋄]), abbreviated APLAN parallel to JSON, is a way to write most arrays literally, with no or minimal use of primitive functions, possibly over multiple code lines. It differs from the strand notation existing since APL\360 in that it can be used to write arrays of rank greater than one. Array notation is supported in dzaima/APL, BQN (using angle brackets ⟨⋄⟩ instead of round parentheses (⋄)), and some tools for Dyalog APL, where it is planned as an eventual language feature.
Array notation generally consists of a vector notation written with parentheses (), roughly equivalent to stranding, and a high-rank notation using square brackets [], indicating the Mix of a vector. It also supports namespaces, using name:value syntax in round parentheses. Statement separators must appear between elements and between name–value pairs.
Examples
Medium-sized array constants are often needed in code. Due to the lack of a native multi-line notation, programmers have resorted to various ad-hoc methods of approximating such, usually at the cost of reduced readability. A very common technique is repeated concatenation resulting in the desired value being held in a variable (z in the below examples), as opposed to array notation which can express the final value directly. In addition, the traditional technique sometimes involves the creation of helper variables as a side effect.
Basic arrays
| Traditional method | Array notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
(0 6 1 8)(1 4 1 4 2)(2 7 1 8 2 8)(3 1 4 1 5) |
(0 6 1 8 ⋄ 1 4 1 4 2 ⋄ 2 7 1 8 2 8 ⋄ 3 1 4 1 5) |
Vector of numeric vectors on a single line. |
z← (0 6 1 8)(1 4 1 4 2) z,←(2 7 1 8 2 8)(3 1 4 1 5) |
(0 6 1 8 ⋄ 1 4 1 4 2 2 7 1 8 2 8 ⋄ 3 1 4 1 5) |
Vector of numeric vectors split over two lines. |
z←,⊂'Three' z,←⊂'Blind' z,←⊂'Mice' |
('Three'
'Blind'
'Mice')
|
Vector of character vectors, one on each line. (The traditional method includes an unnecessary , to indicate that z will be a vector.)
|
z←⍉⍪0 6 1 8 z⍪← 1 4 1 4 z⍪← 2 7 1 8 z⍪← 3 1 4 2 |
[0 6 1 8 1 4 1 4 2 7 1 8 3 1 4 2] |
Numeric matrix. |
z←⍪10 z⍪←20 z⍪←30 z⍪←40 |
[10 20 30 40] |
Column matrix. |
Involved arrays
| Traditional method | Array notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
a←⍉⍪0 0 1 a⍪← 1 0 1 a⍪← 0 1 1 z←,⊂a a←⍉⍪0 1 1 a⍪← 1 1 0 a⍪← 0 1 0 z,←⊂a a←⍉⍪0 1 1 1 a⍪← 1 1 1 0 z,←⊂a a←⍉⍪0 1 1 0 a⍪← 1 0 0 1 a⍪← 0 1 1 0 z,←⊂a |
([0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1] [0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0] [0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0] [0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0]) |
Vector of matrices. |
z←⍉⍪0 'OK' z⍪← 1 'WS FULL' z⍪← 2 'SYNTAX ERROR' z⍪← 3 'INDEX ERROR' z⍪← 4 'RANK ERROR' |
[0 'OK' 1 'WS FULL' 2 'SYNTAX ERROR' 3 'INDEX ERROR' 4 'RANK ERROR'] |
Table with numeric and text columns. |
a←⍉⍪3 1 4 a⍪← 1 5 0 a←↑a b←⍉⍪2 7 0 b⍪← 2 0 0 z←a,[0.5] b |
[[3 1 4 1 5 0] [2 7 0 2 0 0]] |
Rank 3 numeric array. |
a←,⊂3 1 4 a,←⊂1 5 a←↑a b←,⊂2 7 b,← 2 b←↑b z←↑a b |
[[3 1 5 9] [2 7 2]] |
Rank 3 numeric array relying on automatic padding with fill element. |
z←⍉⍪'fns' ((0 1)(0.7 0)(0.7 0)×size) z⍪← 'fnd' ((0 1)(0 0)(0 0)×size) z⍪← 'lines'((0 0)(0.7 0)(0.7 0)×size) z⍪← 'lnd' ((0 0)(0 0)(0 0)×size) |
['fns' ((0 1 ⋄ 0.7 0 ⋄ 0.7 0)×size) 'fnd' ((0 1 ⋄ 0 0 ⋄ 0 0)×size) 'lines'((0 0 ⋄ 0.7 0 ⋄ 0.7 0)×size) 'lnd' ((0 0 ⋄ 0 0 ⋄ 0 0)×size)] |
Matrix of simple and nested vectors, with dynamic values. |
Namespaces
| Traditional method | Array notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
⎕NS⍬ |
() |
Empty namespace. |
⎕NS¨⍬⍬⍬or (⎕NS⍬)(⎕NS⍬)(⎕NS⍬) |
()()() |
Vector of namespaces. |
z←⎕NS⍬ z.x←'hello' |
(x:'hello') |
Namespace with character vector member. |
z←⎕NS⍬ z.x←⍉⍪'hello' z.x⍪← 'world' |
(x:['hello'
'world'])
|
Namespace with character matrix member. |
z←⎕NS⍬ z.y←⎕NS⍬ z.y.x←⍉⍪'hello' z.y.x⍪← 'world' |
(y:(x:['hello'
'world']))
|
Nested namespace structure with matrix member. |
z←⎕NS⍬ z.f←+ a←⎕NS⍬ a.f←- z,←a a←⎕NS⍬ a.f←× z,←a a←⎕NS⍬ a.f←÷ z←z.f |
((f:+)(f:-)(f:×)(f:÷)).f |
Function array. |
Specification
The notation consists of syntax that was invalid before its introduction, thus causing no issues for backwards compatibility. The added syntax consists of three constructs that are currently SYNTAX ERRORs:
- broken round parentheses:
(…) - broken square brackets:
[…] - empty round parentheses:
()
where broken means interrupted by one or more diamonds (⋄) or line breaks (outside of dfns).
- A broken round parenthesis creates a namespace if every diamond/line break-separated statement is a name-value pair.
- A broken round parenthesis creates a vector if every diamond/line break-separated statement is a value expression. In that case, every such statement forms an element in the resulting vector.
- A broken square bracket creates a an array where every diamond/line break-separated statement forms a major cell in the resulting array.*
()creates a new namespace — equivalent to(⎕NS 0⍴⊂'')- A name-value pair consists of a valid APL identifier, followed by a colon (
:) and a value expression.
* This rule is followed strictly in dzaima/APL, while Dyalog APL considers each statement to have a rank of at least 1, even if it is a scalar.
Formal syntax
The array notation can be described using Extended Backus–Naur form, where an expression is any traditional APL expression:
value ::= expression | list | block | space
list ::= '(' ( ( value sep )+ value? | ( sep value )+ sep? ) ')'
block ::= '[' ( ( value sep )+ value? | ( sep value )+ sep? ) ']'
space ::= '(' sep? ( name ':' value ( sep name ':' value )* )? sep? ')'
sep ::= [⋄#x000A#x000D#x0085]+
History
- See also the Array notation design considerations#Timeline
One-dimensional list syntax with surrounding brackets and delimiters, matching sequence notation in mathematics, is common in programming. It appears as early as ALGOL 68 with parentheses, and square-bracket lists feature in languages from the 1970s such as ML and Icon. MATLAB uses matrix syntax with square brackets, semicolons to separate rows, and commas to separate elements within a row. FP uses angle brackets for lists, and square brackets for function "construction", with behavior like function arrays.
List notation appears in Nial using brackets and commas like [a,b,c], and allowing function arrays called "atlases". A+ and K have a list notation using parentheses and semicolons like (a;b;c). In A+ this is related to bracket indexing and an "expression group" notation written with curly braces and semicolons. It allows line breaks, but in addition to rather than in place of semicolons. The later K version corresponds more closely to APL: the semicolon is a statement separator and is interchangeable with a line break, and because K represents arrays with nested lists, it corresponds to both vector and high-rank array notation.
The first published proposals that influenced Dyalog APL's array notation were made by Phil Last at Dyalog '15 and later in Vector Journal.[1][2] Last cited the syntax of dfns as a sequence of expressions with enclosing braces, as well as APL#'s namespace notation enclosed in double brackets [[]], as precursors. He also used the design in Acre Desktop, a project manager for Dyalog APL, to support storing constant arrays and namespaces in text files. Following the conference presentation, Adám Brudzewsky began work on array notation and presented on it in a series of conferences, initially using parentheses for the high-rank notation[3] and later returning to square brackets.[4][5] Because Last's use of ← to separate namespace keys from values prevented lists from including arbitrary expressions (which might contain assignment), he proposed a change to : as in JSON. Dyalog APL 18.0, released in 2020, included support for array notation in source files loaded by Link[6], but not in the language itself.[7]
The project manager Acre Desktop added support for the non-namespace parts of the notation in early 2018, together with Phil Last's original namespace notation, using square brackets and assignment arrow. dzaima/APL added support for vector notation with parentheses in 2018, namespaces and function arrays in 2019, and high-rank arrays with square brackets in 2020. BQN supported lists with angle brackets (⟨…⟩) in its initial implementation in 2020; square brackets ([…]) were reserved for high-rank array notation, which was implemented in 2022.
On April 21, 2023, Dyalog Ltd published a blog post by Morten Kromberg announcing to the community the formal proposal for an APL array notation[8] and by May 5, the specification for scoping in namespaces was changed due to feedback from Dyalog Ltd employee Peter Mikkelsen: Assignments inside value expressions would now affect the surrounding scope rather than having dfn-like auto-localisation, which can instead be achieved by wrapping the expression in an anonymous dfn.
Comparison of array notations
The following systems support list or vector notation in some form, beyond simple strand notation. The separators ; in A+ and K, and ⋄ in APL and BQN, indicate any separator, including a line break.
| System | Vectors | High-rank | Namespaces | Function arrays | Assignable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nial | [,] |
No | N/A | Special | No |
| A+ | (;) |
No | N/A | First-class | Yes |
| K | (;) |
N/A | [key:val;] |
First-class | Yes |
| BQN[9] | ⟨⋄⟩ |
[⋄] |
{key⇐val⋄} |
First-class | Yes |
| dzaima/APL | (⋄) |
[⋄] |
(key:val⋄) |
Special | No |
| Dyalog Link | (⋄) |
[⋄] |
(key:val⋄) |
No | No |
| Acre Desktop[10] | (⋄) |
[⋄] |
[key←val⋄] |
No | N/A |
| TinyAPL | ⟨⋄⟩ |
[⋄] |
⦃key←val⋄⦄ |
First-class | Yes |
Nial and A+ do not support namespaces, while K does not support high-rank arrays, so any such notation is not applicable. The "Function arrays" column indicates whether functions can be placed in array notation. "First class" indicates that functions are first class, so this is possible without special consideration. "Special" indicates creating a special vectors of functions that can be applied to arguments to return a list of results. The "Assignable" column indicates that array notation can be used as an assignment target to perform destructuring. BQN's namespaces don't use a dedicated construction; instead, any block (like a dfn) with ⇐ statements returns a namespace reference. Acre Desktop only uses array notation for storing literal arrays; it cannot appear in executable code.
Documentation
External links
- Formal Proposal document
- Evaluate APL Array Notation sandbox
References
- ↑ Phil Last. APL Array Notation (transcript). Dyalog '15.
- ↑ Phil Last. A Notation for APL array Embedding and Serialization. Vector Journal, Volume 26, number 4. British APL Association. 2016.
- ↑ Adám Brudzewsky. Literal Notation for Arrays and Namespaces (slides). Dyalog '17.
- ↑ Adám Brudzewsky. Array Notation Mk III. Dyalog '18.
- ↑ Adám Brudzewsky. A Notation for APL Arrays. APL-Journal, Volume 2020, number 1-2. APL-Germany e.V. 2020.
- ↑ Dyalog Ltd. Link User Guide: Creating APL Source Files and Directories. Retrieved 2022-08-24.
- ↑ Adám Brudzewsky. Array Notation RC1 (slides). Dyalog '20.
- ↑ Kromberg, Morten. Formal Proposal for APL Array Notation – Seeking Feedback. Formal Proposal for APL Array Notation – Seeking Feedback. April 21, 2023.
- ↑ Lochbaum, Marshall. BQN: Array notation and display; Array literals. Retrieved 2022-09-01.
- ↑ The Carlisle Group. APL Array Notation. Acre Desktop Wiki. GitHub. Retrieved 2022-09-01.